Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq
DNA methylation is a post-replication chemical modification of cytosines (5mC) at CpG loci. The state of DNA methylation is variable along the genome and can significantly modify the expression of specific genes and affect chromatin remodeling.
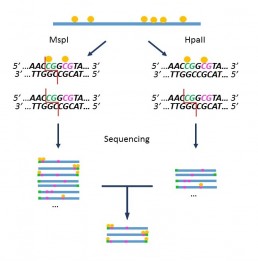
“Methyl Seq” is a DNA methylation evaluation method that exploits the differential activity of the restriction enzymes MspI and HpaII according to the methylation status of their restriction sites (AL Brunner et al). Although it has some limitations (only detects CpG sites included in restriction sites), this method reflects the global methylation of the genome.
The sample is split into 2 aliquots, one incubated with MspI which digests the restriction site regardless of the methylation state of the cytosines, the other with HpaII which digests only non-methylated sites. After ends repair, the fragments are indexed with the adaptors required for NGS sequencing.
The comparative analysis of sequencing data allows the identification of sequences derived from methylated sites.
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- BiSeq