Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
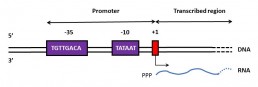
A transcription start site (TSS) is the location where the first DNA nucleotide is transcribed into RNA. It is difficult to determine the exact position of the TSS using bioinformatics, but experimental methods can be used to locate it, notably high throughput sequencing.
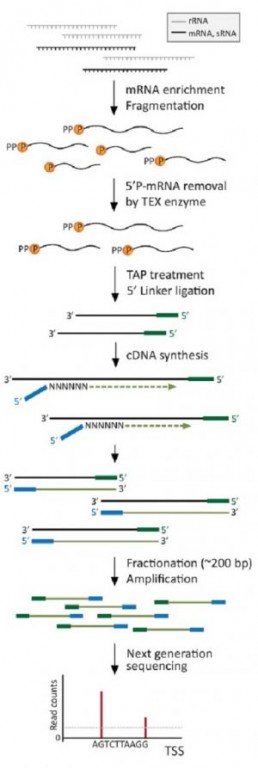
The TSS mapping protocol uses TAP or “Tobacco Acid Pyrophosphatase”, an enzyme that converts the 5′ PPP ends of native RNAs into 5′ P ends, compatible with adapter ligation.
The study is performed by comparing the sequencing results of the 5′ ends of RNAs treated or not with TAP. Without TAP, sequencing will give access to all RNAs (messenger RNAs mature or in process of degradation ) except those with native 5′ ends. After TAP treatment, the same sequences will be obtained, with the additional sequences of the native RNA (S Cho et al.).
Platforms to contact
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq
- BiSeq